Study guide: Scientific software engineering; wave equation model
Oct 20, 2015
Migrating loops to Cython
- Vectorization: 5-10 times slower than pure C or Fortran code
- Cython: extension of Python for translating functions to C
- Principle: declare variables with type
Declaring variables and annotating the code
Pure Python code:
def advance_scalar(u, u_1, u_2, f, x, y, t,
n, Cx2, Cy2, dt2, D1=2, D2=1):
Ix = range(0, u.shape[0]); Iy = range(0, u.shape[1])
for i in Ix[1:-1]:
for j in Iy[1:-1]:
u_xx = u_1[i-1,j] - 2*u_1[i,j] + u_1[i+1,j]
u_yy = u_1[i,j-1] - 2*u_1[i,j] + u_1[i,j+1]
u[i,j] = D1*u_1[i,j] - D2*u_2[i,j] + \
Cx2*u_xx + Cy2*u_yy + dt2*f(x[i], y[j], t[n])
- Copy this function and put it in a file with
.pyxextension. - Add type of variables:
-
function(a, b)\( \rightarrow \)cpdef function(int a, double b) -
v = 1.2\( \rightarrow \)cdef double v = 1.2 - Array declaration:
np.ndarray[np.float64_t, ndim=2, mode='c'] u
Cython version of the functions
import numpy as np
cimport numpy as np
cimport cython
ctypedef np.float64_t DT # data type
@cython.boundscheck(False) # turn off array bounds check
@cython.wraparound(False) # turn off negative indices (u[-1,-1])
cpdef advance(
np.ndarray[DT, ndim=2, mode='c'] u,
np.ndarray[DT, ndim=2, mode='c'] u_1,
np.ndarray[DT, ndim=2, mode='c'] u_2,
np.ndarray[DT, ndim=2, mode='c'] f,
double Cx2, double Cy2, double dt2):
cdef int Nx, Ny, i, j
cdef double u_xx, u_yy
Nx = u.shape[0]-1
Ny = u.shape[1]-1
for i in xrange(1, Nx):
for j in xrange(1, Ny):
u_xx = u_1[i-1,j] - 2*u_1[i,j] + u_1[i+1,j]
u_yy = u_1[i,j-1] - 2*u_1[i,j] + u_1[i,j+1]
u[i,j] = 2*u_1[i,j] - u_2[i,j] + \
Cx2*u_xx + Cy2*u_yy + dt2*f[i,j]
Note: from now in we skip the code for setting boundary values
Visual inspection of the C translation
See how effective Cython can translate this code to C:
Terminal> cython -a wave2D_u0_loop_cy.pyx
Load wave2D_u0_loop_cy.html in a browser (white lines
indicate code that was successfully translated to pure C, while
yellow lines indicate code that is still in Python):
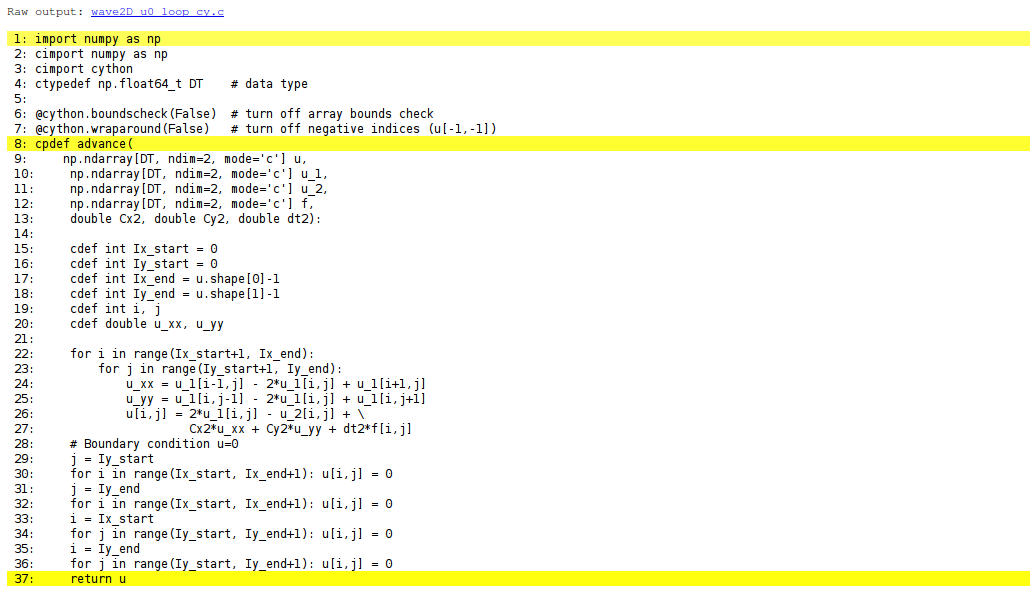
Can click on wave2D_u0_loop_cy.c to see the generated C code...
Building the extension module
- Cython code must be translated to C
- C code must be compiled
- Compiled C code must be linked to Python C libraries
- Result: C extension module (
.sofile) that can be loaded as a standard Python module - Use a
setup.pyscript to build the extension module
from distutils.core import setup
from distutils.extension import Extension
from Cython.Distutils import build_ext
cymodule = 'wave2D_u0_loop_cy'
setup(
name=cymodule
ext_modules=[Extension(cymodule, [cymodule + '.pyx'],)],
cmdclass={'build_ext': build_ext},
)
Terminal> python setup.py build_ext --inplace
Calling the Cython function from Python
import wave2D_u0_loop_cy
advance = wave2D_u0_loop_cy.advance
...
for n in It[1:-1: # time loop
f_a[:,:] = f(xv, yv, t[n]) # precompute, size as u
u = advance(u, u_1, u_2, f_a, x, y, t, Cx2, Cy2, dt2)
Efficiency:
- \( 120\times 120 \) cells in space:
- Pure Python: 1370 CPU time units
- Vectorized
numpy: 5.5 - Cython: 1
- \( 60\times 60 \) cells in space:
- Pure Python: 1000 CPU time units
- Vectorized
numpy: 6 - Cython: 1
Migrating loops to Fortran
- Write the
advancefunction in pure Fortran - Use
f2pyto generate C code for calling Fortran from Python - Full manual control of the translation to Fortran
The Fortran subroutine
subroutine advance(u, u_1, u_2, f, Cx2, Cy2, dt2, Nx, Ny)
integer Nx, Ny
real*8 u(0:Nx,0:Ny), u_1(0:Nx,0:Ny), u_2(0:Nx,0:Ny)
real*8 f(0:Nx, 0:Ny), Cx2, Cy2, dt2
integer i, j
Cf2py intent(in, out) u
C Scheme at interior points
do j = 1, Ny-1
do i = 1, Nx-1
u(i,j) = 2*u_1(i,j) - u_2(i,j) +
& Cx2*(u_1(i-1,j) - 2*u_1(i,j) + u_1(i+1,j)) +
& Cy2*(u_1(i,j-1) - 2*u_1(i,j) + u_1(i,j+1)) +
& dt2*f(i,j)
end do
end do
Note: Cf2py comment declares u as input argument and return value
back to Python
Building the Fortran module with f2py
Terminal> f2py -m wave2D_u0_loop_f77 -h wave2D_u0_loop_f77.pyf \
--overwrite-signature wave2D_u0_loop_f77.f
Terminal> f2py -c wave2D_u0_loop_f77.pyf --build-dir build_f77 \
-DF2PY_REPORT_ON_ARRAY_COPY=1 wave2D_u0_loop_f77.f
f2py changes the argument list (!)
>>> import wave2D_u0_loop_f77
>>> print wave2D_u0_loop_f77.__doc__
This module 'wave2D_u0_loop_f77' is auto-generated with f2py....
Functions:
u = advance(u,u_1,u_2,f,cx2,cy2,dt2,
nx=(shape(u,0)-1),ny=(shape(u,1)-1))
- Array limits have default values
- Examine doc strings from
f2py!
How to avoid array copying
- Two-dimensional arrays are stored row by row in Python and C
- Two-dimensional arrays are stored column by column in Fortran
-
f2pytakes a copy of anumpy(C) array and transposes it when calling Fortran - Such copies are time and memory consuming
- Remedy: declare
numpyarrays with Fortran storage
order = 'Fortran' if version == 'f77' else 'C'
u = zeros((Nx+1,Ny+1), order=order)
u_1 = zeros((Nx+1,Ny+1), order=order)
u_2 = zeros((Nx+1,Ny+1), order=order)
Option -DF2PY_REPORT_ON_ARRAY_COPY=1 makes f2py write out
array copying:
Terminal> f2py -c wave2D_u0_loop_f77.pyf --build-dir build_f77 \
-DF2PY_REPORT_ON_ARRAY_COPY=1 wave2D_u0_loop_f77.f
Efficiency of translating to Fortran
- Same efficiency (in this example) as Cython and C
- About 5 times faster than vectorized
numpycode - \( >1000 \) faster than pure Python code
Migrating loops to C via Cython
- Write the
advancefunction in pure C - Use Cython to generate C code for calling C from Python
- Full manual control of the translation to C
The C code
-
numpyarrays transferred to C are one-dimensional in C - Need to translate
[i,j]indices to single indices
/* Translate (i,j) index to single array index */
#define idx(i,j) (i)*(Ny+1) + j
void advance(double* u, double* u_1, double* u_2, double* f,
double Cx2, double Cy2, double dt2,
int Nx, int Ny)
{
int i, j;
/* Scheme at interior points */
for (i=1; i<=Nx-1; i++) {
for (j=1; j<=Ny-1; j++) {
u[idx(i,j)] = 2*u_1[idx(i,j)] - u_2[idx(i,j)] +
Cx2*(u_1[idx(i-1,j)] - 2*u_1[idx(i,j)] + u_1[idx(i+1,j)]) +
Cy2*(u_1[idx(i,j-1)] - 2*u_1[idx(i,j)] + u_1[idx(i,j+1)]) +
dt2*f[idx(i,j)];
}
}
}
}
The Cython interface file
import numpy as np
cimport numpy as np
cimport cython
cdef extern from "wave2D_u0_loop_c.h":
void advance(double* u, double* u_1, double* u_2, double* f,
double Cx2, double Cy2, double dt2,
int Nx, int Ny)
@cython.boundscheck(False)
@cython.wraparound(False)
def advance_cwrap(
np.ndarray[double, ndim=2, mode='c'] u,
np.ndarray[double, ndim=2, mode='c'] u_1,
np.ndarray[double, ndim=2, mode='c'] u_2,
np.ndarray[double, ndim=2, mode='c'] f,
double Cx2, double Cy2, double dt2):
advance(&u[0,0], &u_1[0,0], &u_2[0,0], &f[0,0],
Cx2, Cy2, dt2,
u.shape[0]-1, u.shape[1]-1)
return u
Building the extension module
Compile and link the extension module with a setup.py file:
from distutils.core import setup
from distutils.extension import Extension
from Cython.Distutils import build_ext
sources = ['wave2D_u0_loop_c.c', 'wave2D_u0_loop_c_cy.pyx']
module = 'wave2D_u0_loop_c_cy'
setup(
name=module,
ext_modules=[Extension(module, sources,
libraries=[], # C libs to link with
)],
cmdclass={'build_ext': build_ext},
)
Terminal> python setup.py build_ext --inplace
In Python:
import wave2D_u0_loop_c_cy
advance = wave2D_u0_loop_c_cy.advance_cwrap
...
f_a[:,:] = f(xv, yv, t[n])
u = advance(u, u_1, u_2, f_a, Cx2, Cy2, dt2)
Migrating loops to C via f2py
- Write the
advancefunction in pure C - Use
f2pyto generate C code for calling C from Python - Full manual control of the translation to C
The C code and the Fortran interface file
- Write the C function
advanceas before - Write a Fortran 90 module defining the signature of
the
advancefunction - Or: write a Fortran 77 function defining the signature and
let
f2pygenerate the Fortran 90 module
Fortran 77 signature (note intent(c)):
subroutine advance(u, u_1, u_2, f, Cx2, Cy2, dt2, Nx, Ny)
Cf2py intent(c) advance
integer Nx, Ny, N
real*8 u(0:Nx,0:Ny), u_1(0:Nx,0:Ny), u_2(0:Nx,0:Ny)
real*8 f(0:Nx, 0:Ny), Cx2, Cy2, dt2
Cf2py intent(in, out) u
Cf2py intent(c) u, u_1, u_2, f, Cx2, Cy2, dt2, Nx, Ny
return
end
Building the extension module
Generate Fortran 90 module (wave2D_u0_loop_c_f2py.pyf):
Terminal> f2py -m wave2D_u0_loop_c_f2py \
-h wave2D_u0_loop_c_f2py.pyf --overwrite-signature \
wave2D_u0_loop_c_f2py_signature.f
The compile and build step must list the C files:
Terminal> f2py -c wave2D_u0_loop_c_f2py.pyf \
--build-dir tmp_build_c \
-DF2PY_REPORT_ON_ARRAY_COPY=1 wave2D_u0_loop_c.c
Migrating loops to C++ via f2py
- C++ can be used as an alternative to C
- C++ code often applies sophisticated arrays
- Challenge: translate from
numpyC arrays to C++ array classes - Can use SWIG to make C++ classes available as Python classes
- Easier (and more efficient):
- Make C API to the C++ code
- Wrap C API with
f2py - Send
numpyarrays to C API and let C translatenumpyarrays into C++ array classes