Much of the material in this document is taken from Appendix H.1 in the book A Primer on Scientific Programming with Python, 4th edition, by the same author, published by Springer, 2014.
How to write and run a Python program
You have basically three choices to develop and test a Python program:
- use the IPython notebook
- use an Integrated Development Environment (IDE), like Spyder, which offers a window with a text editor and functionality to run programs and observe the output
- use a text editor and a terminal window
The need for a text editor
Since programs consist of plain text, we need to write this text with the help of another program that can store the text in a file. You have most likely extensive experience with writing text on a computer, but for writing your own programs you need special programs, called editors, which preserve exactly the characters you type. The widespread word processors, Microsoft Word being a primary example, are aimed at producing nice-looking reports. These programs format the text and are not acceptable tools for writing your own programs, even though they can save the document in a pure text format. Spaces are often important in Python programs, and editors for plain text give you complete control of the spaces and all other characters in the program file.
Spyder
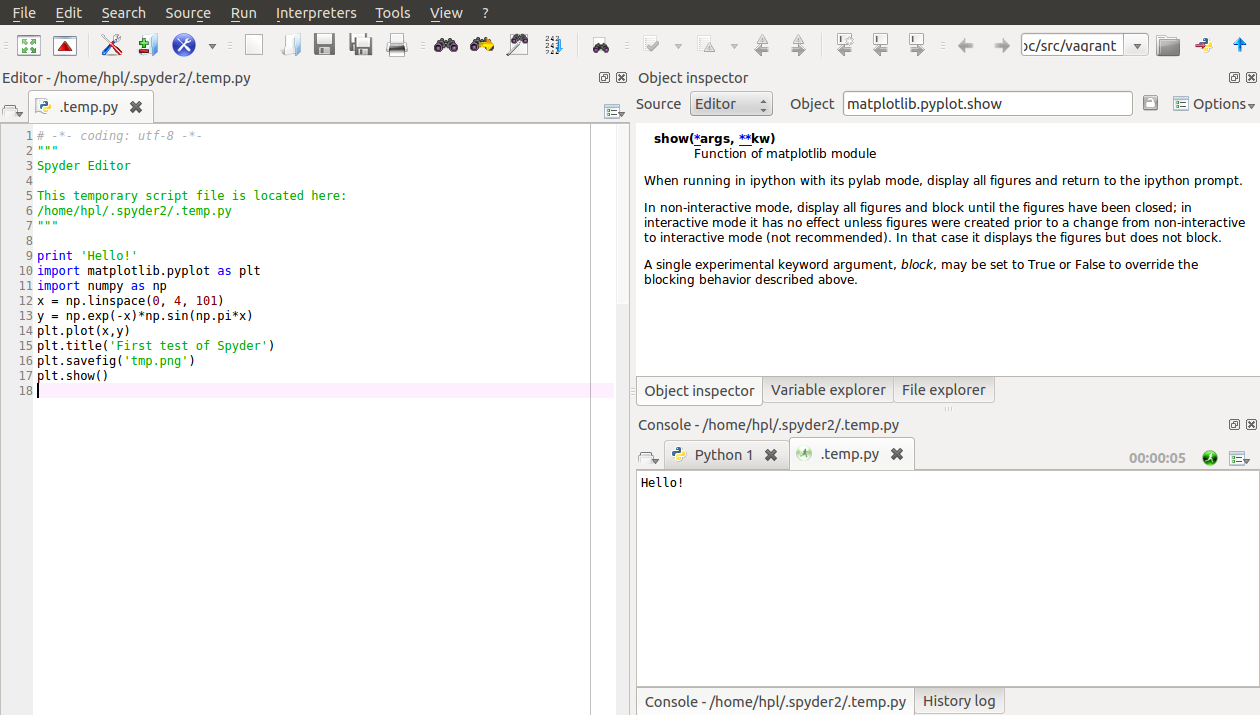
Spyder is graphical application for developing and running Python
programs, available on all major platforms. Spyder comes with Anaconda
and some other pre-built environments for scientific computing with
Python. On Ubuntu it is conveniently installed by sudo apt-get
install spyder.
The left part of the Spyder window contains a plain text editor.
Click in this window and write print 'Hello!' and return.
Choose Run from the Run pull-down menu, and observe the output
Hello! in the lower right window where the output from
programs is visible.
You may continue with more advanced statements involving graphics:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 4, 101)
y = np.exp(-x)*np.sin(np.pi*x)
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.title('First test of Spyder')
plt.savefig('tmp.png')
plt.show()
Choosing Run - Run now leads to a separate window with a plot of the function \( e^{-x}\sin (\pi x) \). Figure 1 shows how the Spyder application may look like.
Figure 1: The Spyder Integrated Development Environment.
The plot file we generate in the above program,
tmp.png, is by default found in the Spyder folder listed in
the default text in the top of the program. You can choose
Run - Configure ... to change this folder as desired.
The program you write is written to a file .temp.py in the same
default folder, but any name and folder can be specified in the
standard File - Save as... menu.
A convenient feature of Spyder is that the upper right window continuously displays documentation of the statements you write in the editor to the left.
Text editors
The most widely used editors for writing programs are Emacs and Vim, which are available on all major platforms. Some simpler alternatives for beginners are
- Linux: Gedit
- Mac OS X: TextWrangler
- Windows: Notepad++
Gedit is a standard program on Linux platforms, but all other editors must installed in your system. This is easy: just google for the name, download the file, and follow the standard procedure for installation. All of the mentioned editors come with a graphical user interface that is intuitive to use, but the major popularity of Emacs and Vim is due to their rich set of short-keys so that you can avoid using the mouse and consequently edit at higher speed.
Terminal windows
To run the Python program, you need a terminal window. This is a
window where you can issue Unix commands in Linux and Mac OS X systems
and DOS commands in Windows. On a Linux computer, gnome-terminal
is my favorite, but other choices work equally well, such as xterm
and konsole. On a Mac computer, launch the application Utilities -
Terminal. On Windows, launch PowerShell.
You must first move to the right folder using the cd foldername
command. Then running a python program prog.py is a matter of
writing python prog.py. Whatever the program prints can be
seen in the terminal window.
Using a plain text editor and a terminal window
- Create a folder where your Python programs can be located, say
with name
mytestunder your home folder. This is most conveniently done in the terminal window since you need to use this window anyway to run the program. The command for creating a new folder ismkdir mytest. - Move to the new folder:
cd mytest. - Start the editor of your choice.
- Write a program in the editor, e.g., just the line
print 'Hello!'. Save the program under the namemyprog1.pyin themytestfolder. - Move to the terminal window and write
python myprog1.py. You should see the wordHello!being printed in the window.